What is tissue expansion?
Tissue expansion is a relatively straightforward procedure that enables the body to “grow” extra skin for use in reconstructing almost any part of the body.
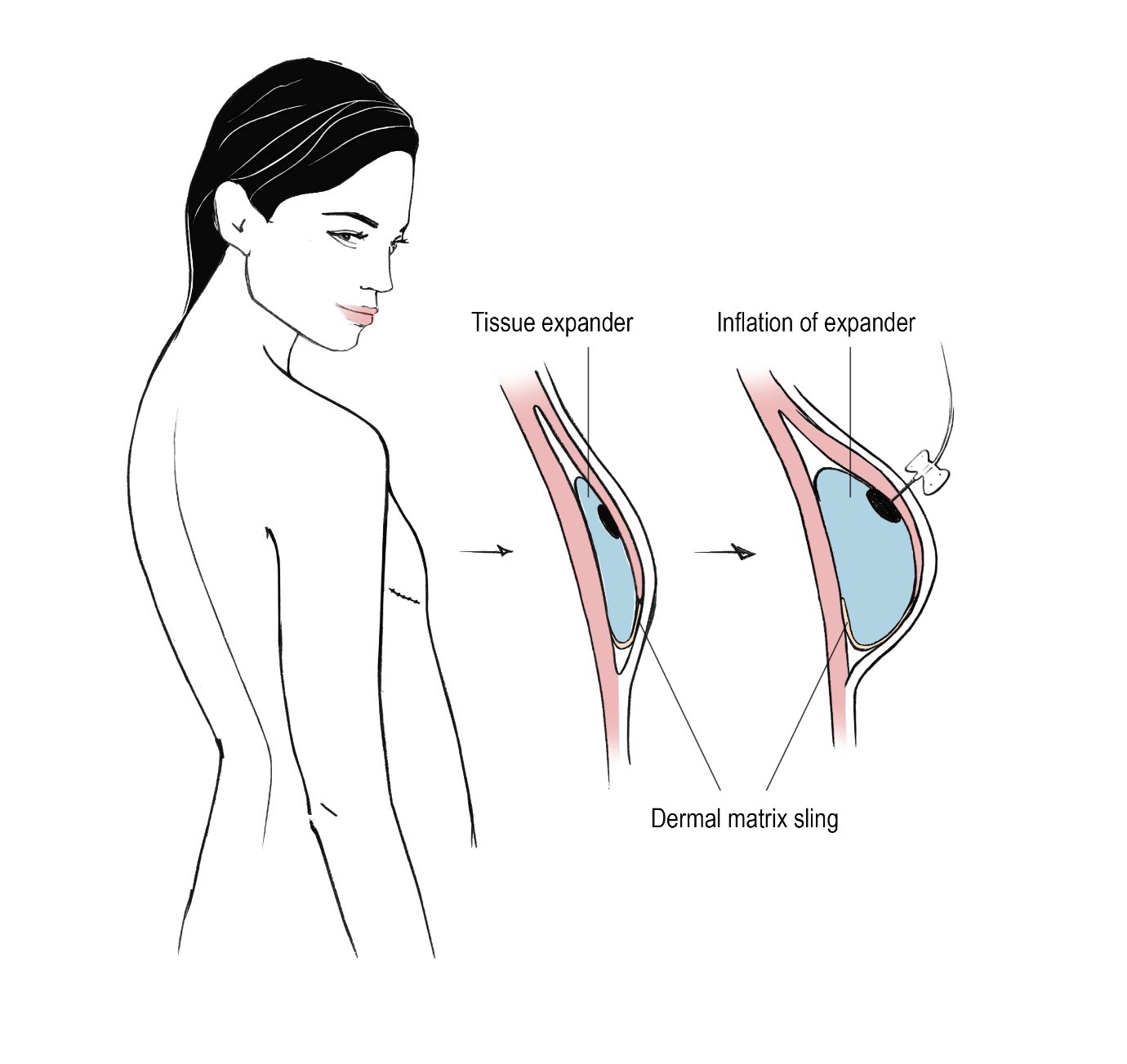
A silicone balloon expander is inserted under the skin near the area to be repaired and then gradually filled with saline or carbon dioxide over time, causing the skin to stretch and grow. It is most commonly used for breast reconstruction following breast removal, but it’s also used to repair skin damaged by birth defects, accidents, surgery and in certain cosmetic procedures.
If your doctor is recommending tissue expansion, this will give you a basic understanding of the procedure – when it can help, how it’s performed and what results you can expect. It can’t answer all of your questions, however, since much depends on your individual circumstances. Please be sure to ask your surgeon if there is anything you don’t understand about the procedure.
Why Iran for tissue expander procedure?
Iran is known to be one of the best countries that provide medical services. The rate of successful surgeries performed in Iran is very high. The medical institutions in Iran are well equipped with the newest medical devices and tools. In addition, the Iranian surgeons and doctors are professional and highly experienced, especially in reconstruction procedures such as tissue expander procedure.
How much does tissue expander cost in Iran?
The costs of medical surgeries and procedures in Iran are very reasonable when compared with their prices in Western developed countries, even though they are performed by professional surgeons. The most important reason for the decline in these prices in Iran is the depreciation of the national currency with respect to foreign currencies.
Placing your tissue expander
There are 2 ways to place your tissue expander:
- Submuscular placement is when your surgeon places the expander under your large pectoralis muscle in your chest. They will make a pocket under the muscle and place your tissue expander in that space.
If your tissue expander is under your muscle, it will be filled with liquid. Your skin is very weak and fragile after your mastectomy. Your muscle is a barrier between your skin and the tissue expander. It helps take the pressure from the expander off your skin when it’s healing.
- Prepectoral placement is when your surgeon places the expander over your large pectoralis muscle in your chest. They will also place a mesh called acellular dermal matrix around the expander. The mesh will help support the expander while your skin is healing. Over time, your body will absorb the mesh. It will not need to be removed.
If your tissue expander is over your muscle, it may first be filled with air instead of liquid. Your skin is very weak and fragile after your mastectomy. Because air is less dense than water, it will put less pressure on your skin when it’s first healing. Your surgeon will replace the air in your tissue expander with liquid about 2 weeks after your surgery.
WHO MAKES A CANDIDATE FOR TISSUE EXPANDER?
If you have a condition that requires additional skin to treat deformities whether congenital or caused by an incidence or a previous surgery, then you are considered as a candidate for tissue expander procedure. This surgery can be done for all ages from babies to older men and women.
This surgical procedure is widely used for breast reconstruction, mainly after breast resection, when there is not enough skin to place a permanent breast implant and restore the natural appearance of the breasts.
Tissue expander is also an option to repair or replace the scalp. Due to the growth of hair in this area, it is difficult to replace the skin from other parts of the body.
In general, tissue expansion technique (tissue expander) has excellent results and it is used when some areas of the face, neck, breast, arms and legs need to be reconstructed.
It is somewhat more difficult to expand the tissue on the waist or other areas of the body that have thick skin. If the area is severely damaged or scarred, the tissue expansion technique is usually not suitable because there is no healthy skin to expand the tissue.
HOW DO I KNOW IF TISSUE EXPANDER IS SUITABLE FOR ME?
During the first consultation, the surgeon examines the patient. The patient’s age, skin condition, medical history and other factors are checked to help the surgeon obtain the correct information for this surgery.
The diseases you previously suffered from and their effect on the success of the procedure are another factors that determine whether tissue expander is the best solution for your condition or not.
The patient’s flexibility, patience and endurance are also very important in this surgical method. Before performing this technique, talk to your surgeon about your expectations and goals and get a comprehensive view of the surgery.
How is the procedure performed?
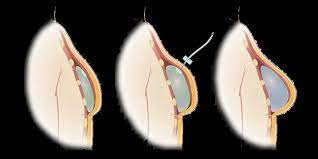
Tissue expansion is accomplished by placing a balloon like expander underneath the skin near the damaged region. Over time, the expander is filled with saline (or saltwater) solution causing the skin around it to stretch and grow. Once the new skin has reached its ideal size the tissue expander is removed and the new skin is redistributed, replacing the damaged area of skin.
When is tissue expansion recommended? What are the benefits?
Tissue expansion to regions of the face, neck, arms, hands, and legs normally lead to excellent results. When skin thickness is greater, like on the back and torso, expansion is more difficult. Since healthy skin is the primary requirement, expansion is usually not an option for areas where the skin is severely damaged or scarred. Your surgeon will discuss your options with you.
Tissue expansion allows for the growth of new skin. Without tissue expansion, other procedures are performed to use existing skin in other parts of the body for reconstruction. Using tissue expansion instead of existing skin, like flaps or skin grafts, usually leads to better outcomes. Since the skin remains connected to the same blood and nerve supply, unlike in most skin flap or skin graft procedures, there is less of a risk for the new skin to have side effects, including skin death. The grown skin is a better match cosmetically, having the same color, texture and hair qualities as the issue area. Scars are also often less visible because skin doesn’t have to be moved from one area to another.
If you need tissue expansion surgery
You and your surgeon will reach an understanding about what you can expect from this procedure and the long-term benefits you will experience. Every patient is different, and your surgeon will choose the surgical technique and treatment plan that is right for you. During the initial consultation, you should expect to provide a complete medical history and have measurements and photographs taken for your medical record. Your surgeon will conduct a complete physical examination and discuss possible risks and complications of the procedure.
If you choose to have surgery at U of M, you will be given a pre-operative information packet that explains everything you should do and know before your surgery date. Your surgeon will give you specific instructions on how to prepare for surgery, including guidelines on eating and drinking, smoking, and taking or avoiding certain vitamins and medications. Your procedure will take place at the University of Michigan Hospitals, which provides state-of-the-art surgical suites and recovery areas. The majority of these procedures do not require an overnight stay in the hospital.
What to Expect During Your Tissue Expansions
During your second or third office visit, you’ll have your first tissue expansion.
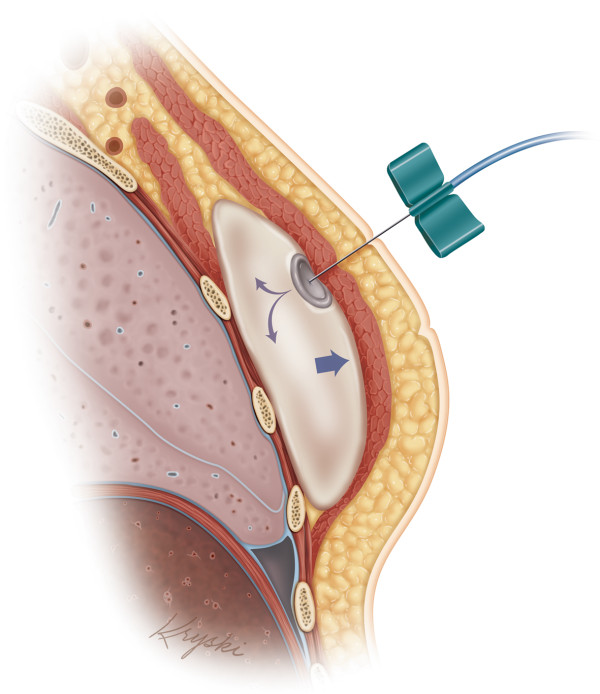
- If your tissue expander is under your muscle, your nurse will inject liquid into it through the port. They’ll use a small needle.
- If your tissue expander is over your muscle and has air in it, your nurse will remove the air. They’ll replace the air with liquid.
- If your tissue expander is over your muscle and has liquid in it, your nurse will add more.
You’ll have a tissue expansion visit about every week or every other week. The tissue expansion procedure only takes a few minutes. Your reconstructed breast will get bigger after each expansion. It will not take its final form until the permanent implant is placed.
How to be more comfortable between tissue expansions
After each expansion, you may feel some tightness and fullness in your breast. You may also have some discomfort in your shoulder or back. This most often gets better within a few days.
After your expansion your chest may be sore, like after you have exercised. Here are some things you can do to be more comfortable between tissue expansions:
- Take a few warm showers a day to help relax your muscles.
- Take over-the-counter pain medications (medication you buy without a prescription), such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen
- Use a fragrance-free moisturizer on your breast skin. Do not put it right on your incision for 6 weeks after your surgery or until the scabbing has fully healed.
- Do the arm and shoulder exercises your nurse tells you to do. They’ll give you a written resource with instructions. You can also find the written resources online at www.mskcc.org/pe/exercises_after_mastectomy. You may find it easier to do these stretches after you shower since your muscles will be more relaxed.
- Wear soft, supportive bras. Do not wear underwire bras.