OVULATION INDUCTION
Ovulation induction is the process of using medications to stimulate ovulation in women who have irregular or absent ovulation (anovulation). According to the National Institutes of Health, 25 to 30 percent of women with infertility have problems with ovulation.
Normal ovulation occurs when the ovary releases a mature egg in preparation for that egg to be fertilized. Normal ovulation occurs roughly once every 28 days during a woman’s menstrual cycle. Intervals of 21 to 35 days are considered acceptable and reflective of normal ovulation. If fertilization does not occur, the mature egg and any supplementary tissues are broken down and cleared from the uterus naturally.
When ovulation happens less than once every 35 days or is unpredictable, it is considered to be irregular. When ovulation is completely unpredictable – in interval or duration – it is considered oligoovulation. If it doesn’t occur at all, it is called anovulation. Ovulatory problems impact fertility by taking away the predictability of ovulation and potentially the availability of an egg to be fertilized.
The goal of ovulation induction is to increase a woman’s chances of conceiving a child, either through sexual intercourse or by using intrauterine insemination (IUI) or another fertility treatment. However, when the absence of ovulation is a symptom of another fertility issue, treating the underlying problem can also restore normal ovulation and fertility.
Medications used for ovulation induction
Ovulation induction uses a variety of hormone-based medications to regulate a woman’s reproductive hormones and increase the chances of ovulation. Some of the commonly used medications are:
- Clomiphen citrate: Stimulates ovulation in women who have normal pituitary (a gland in the brain) hormones but in whom the normal monthly changes in these hormones are not occurring. Most patients know this medication by its brand name Clomid.
- Aromatase inhibitors: With similar indications as for clomiphene citrate, this type of medication is very effective in patients with PCOS. Most patients know this medication as letrozole or by the brand name Femara.
- Insulin-sensitizing agents: These are used in some PCOS patients who have evidence of diabetes or prediabetes. Most patients know this medication as metformin.
- Gonadotropins: Consist of two injectable hormones, luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), that encourage egg development and are normally produced by the pituitary gland. Because of how powerfully gonadotropins stimulate egg development, they require more frequent monitoring than clomiphene citrate and letrozole. Risks include multiple pregnancy and ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS), in which the ovaries become overstimulated and swollen.
In some cases, treating another condition, such as obesity or hypothyroidism, can jump-start ovulation naturally.
Who could benefit from ovulation induction
Ovulation induction is a common treatment for women with absent or infrequent ovulation. Women with ovulation-interrupting disorders such as PCOS can also benefit from ovulation induction.
Ovulation induction also works in conjunction with in vitro fertilization (IVF) by stimulating multiple mature eggs to release for collection and use in lab fertilization. This is typically called controlled ovarian hyperstimulation.
When determining whether or not to use ovulation induction, physicians usually look at:
- Disorders that can directly inhibit normal ovulation such as PCOS.
- A woman’s hormone levels, specifically the presence of FSH), AMH and LH.
- Disorders than can indirectly affect ovulation, such as thyroid disorders, eating disorders and obesity.
- The amount of exercise a woman does.
For women who continue to experience abnormal ovulation after ovulation induction treatment, physicians can also try superovulation. Superovulation uses the human chorionic gonadotropin hormone to induce the release of potential mature eggs in the follicle.
Risks and side effects of ovulation induction
Ovulation induction medications can sometimes cause OHSS. The side effects of OHSS range from mild to severe, and usually fade after a few weeks without treatment. They can include:
- Bloating.
- Nausea.
- Headaches.
- Loss of breath.
- Hot flashes.
- Weight gain.
- Tenderness in the pelvic region.
- Blurry vision.
The ovarian superovulation treatment can cause multiple eggs to release, increasing the chance of multiple fertilized eggs (embryos) and a high-risk pregnancy.
Ovulation Induction Candidates
The following are candidates for ovulation induction:
- Women who ovulate infrequently
- Women who do not ovulate at all (anovulation)
- Women with unknown infertility problems who do ovulate regularly;
These women can benefit from ovulation induction to increase the number of times they ovulate during one cycle to give them better chances to conceive and get pregnant.
- Women who are undergoing IVF treatment to increase their egg production.
Ovulation Induction Methods
There are several methods for ovulation induction, depending on how responsive are the ovaries to each method.
The methods are as follows:
- Ovulation induction using one of the medication regimens, which we will discuss below
- Ovarian drilling
- Metformin (especially prescribed for women with PCOS).
Ovulation induction using medication
Ovulation induction is induced with one of the following drug regimens:
- Clomiphene citrate or Clomid tablets:
How does Clomiphene citrate work?
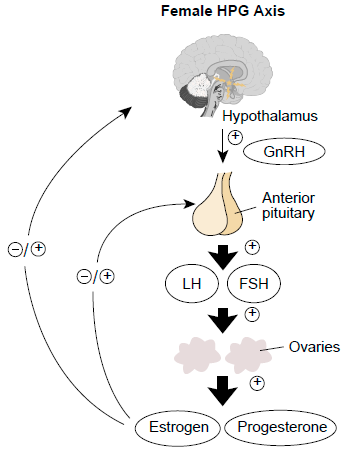
Clomid, also known as Serophene or its alternatives (Tamoxifen and Letrozole tablets) increases the follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and Luteinizing (LH) production by the pituitary gland. Clomiphene works by tricking the body into thinking that it is deficient or low in estrogen. The pituitary gland sends signals to the ovary, after getting impulses from higher centers in the brain, to stimulate the development of the follicles and eggs growth. An LH surge will happen a few days after stopping taking clomiphene citrate, and 36 hours after this surge the patient will start to ovulate.
This tablet is usually given at a starting dose of 50 mg for 5 days of a cycle, usually starting from the second day of the period. Although FDA has approved of a daily intake of 125 mg, the dose will only be increased if the patient does not respond to 50 mg dose and they fail to ovulate; as a result, it will be increased to 100 mg per day. If periods are very irregular and infrequent, in order to induce periods, another tablet regimen might be needed. This tablet is called Norethisterone.
How effective is Clomiphene citrate?
- The effectiveness of Clomid is dependent on a number of reasons, such the age, infertility issues and seminal parameters.
- If a pregnancy is achieved with clomiphene citrate, the chances for twins is about 6- 10% and for triplets or higher is 1% or less.
- Clomiphene side effects
- Clomiphene citrate usually has no immediate serious side effects, but blurred vision, hot flushes, and mood swings may happen.
- Gonadotropins or Gonadotrophins:
How does Gonadotropins work?
This is an injective method of ovulation induction. An injection is done with a small needle daily. These daily self-injections must be continued for 5-12 days. The starting dose varies from patient to patient in order to optimize the probability of conceiving and reduce the chances of multiple pregnancies. The right dosing will be adjusted by monitoring the patient with ultrasound and hormonal evaluation. This injection works by maturing the eggs inside the follicle. Afterward, with an HCG injection which mimics mid-cycle physiologic LH surge, ovulation will happen.
Gonadotrophins are known with these trade names: Gonal F, Menopur, Bravelle, Follistim.
If pregnancy is achieved with this method of ovulation induction, the chances for twins is about 15%, for triplets it goes down to 5% and more less than 1%.
- Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG)
HCG, also known as Novarel, Profasi or Ovidrel is used as an injective ovulation induction method when there are sufficient amounts of matured follicles. With ultrasound, it’s easy to keep track of how responsive is the patient to the drugs. It can then be possible to know when the follicles have grown to their appropriate size, when intercourse is advised and HCG injection might be needed to help with the timing of intercourse or IUI (the process of transferring the semen directly into the uterus). Each patient has different responses to the ovulation induction. The response might be either too strong or not sufficient. In such cases, the current cycle may need to be canceled and a new one will need to be started. If the response turns out to be satisfactory, the treatment can be continued for another 6 consecutive cycles, without break and interruption.
- Letrozole:
Letrozole, also known as Femara, is an oral ovulation induction method. Although this method has not been approved by the FDA, it can be used as an alternative to Clomid (clomiphene citrate), as it has the same results as Clomid. If a patient suffers from Clomid’s side effects, she can alternatively use Letrozole. The starting dose is 2.5 or 5.0 mg, if ovulation does not occur, the dose will be increased by 2.5 mg. Most doctors will not exceed 7.5 mg.
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) analogs:
GnRH analogs, also known as Lupron, Leuprolide Acetate, Ganirelix, Antagon or Cetrotide are similar to GnRH. To control the pituitary gland, GnRH is released by the hypothalamus in the brain. FSH and LH secretion, that are necessary hormones for egg production and subsequent ovulation, is done by stimulating the pituitary gland, which is also a result of a pulsatile release of GnRH hormone. The opposite occurs with synthetic release of GnRH analogs. With Lupron, an FSH and LH suppression happens after an initial increase in those hormones. With Antagon and Cetrotide, immediate suppression might happen. Using GnRH analogs simultaneously with Gonadotrophrine treatment allows for better hormonal control and guarantees more successful results with less failed cycles.
Other ovulation induction options especially for women with PCOS
Women with PCOS who do not ovulate or do not ovulate regularly may be treated with Clomid at first, which in most cases has a satisfactory response. But there are two other options to consider:
– Metformin: PCOS is known for affecting insulin and glucose metabolism. Metformin is a medication used in Diabetes treatment, which on the other hand improves ovulation in some patients with PCOS.
– Ovarian drilling: This is surgical ovulation induction method. In this method about four 4-mm length holes are drilled in the ovary. This method needs laparoscopy and helps women with PCOS to ovulate in 60% to 85% of cases. Scarring rarely happens in this invasive procedure, but it carries the risks of laparoscopy, which are often minor and the serious ones are rare.
Cost in Iran
To compare the ovulation induction cost in Iran with other countries, we take the HCG injection as an example. A course of HCG injection costs around …… in Iran, while an average course of HCG injection in the United Staes costs $400 approximately.