DIABETIC RETINOPATHY TREATMENT
What is diabetic retinopathy?
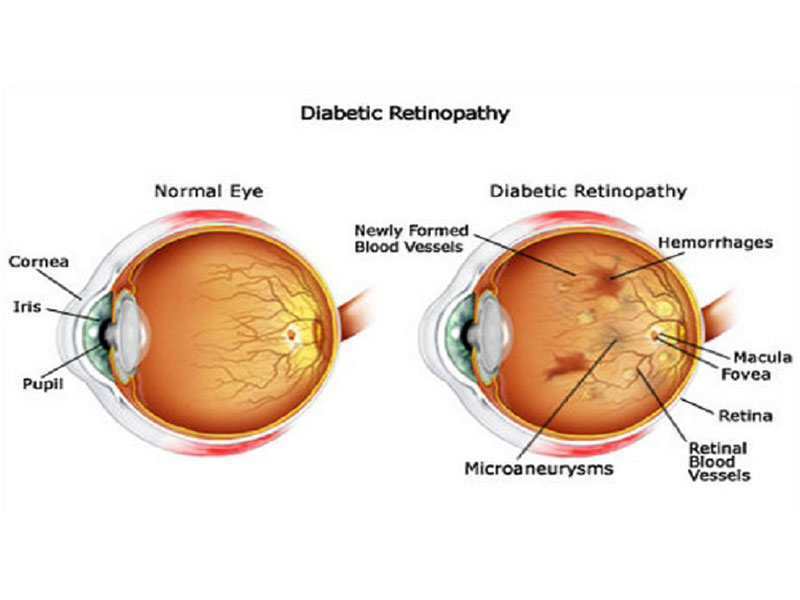
Diabetic retinopathy is an eye condition that can cause vision loss and blindness in people who have diabetes. It affects blood vessels in the retina (the light-sensitive layer of tissue in the back of your eye). If you have diabetes, it’s important to get a comprehensive dilated eye exam at least once a year. Diabetic retinopathy may not have any symptoms at first — but finding it early can help you take steps to protect your vision. Managing your diabetes — by staying physically active, eating healthy, and taking your medicine — can also help you prevent or delay vision loss.
Other types of diabetic eye disease
Diabetic retinopathy is the most common cause of vision loss for people with diabetes. But diabetes can also make you more likely to develop several other eye conditions:
Cataracts: Having diabetes makes you 2 to 5 times more likely to develop cataracts. It also makes you more likely to get them at a younger age.
Open-angle glaucoma: Having diabetes nearly doubles your risk of developing a type of glaucoma called open-angle glaucoma.
What Causes Diabetic Retinopathy?
Diabetic patients suffer from high level of sugar in the blood, which can lead to the blockage of the tiny blood vessels that provide the retina with nutrients. As a result, the eye tries to create new blood vessels. However, these new blood vessels may not develop properly and might leak, which causes diabetic retinopathy.
Who Is at Risk of Diabetic Retinopathy?
Anyone with type 1 diabetes or type 2 diabetes is potentially at risk of developing diabetic retinopathy. However, people with certain health conditions are at a greater risk than others. These conditions include:
1- Being a diabetic patient for a long period of time
2- Having a persistent high blood sugar (blood glucose) level
3- Having high cholesterol level
4- Pregnancy
5- Being of Afro-Caribbean or Asian background
6- Constant Tobacco use
What Are the Complications of Diabetic Retinopathy if Not Treated?
Diabetic retinopathy involves the abnormal growth of blood vessels in the retina, which can lead to serious vision problems if not treated, including:
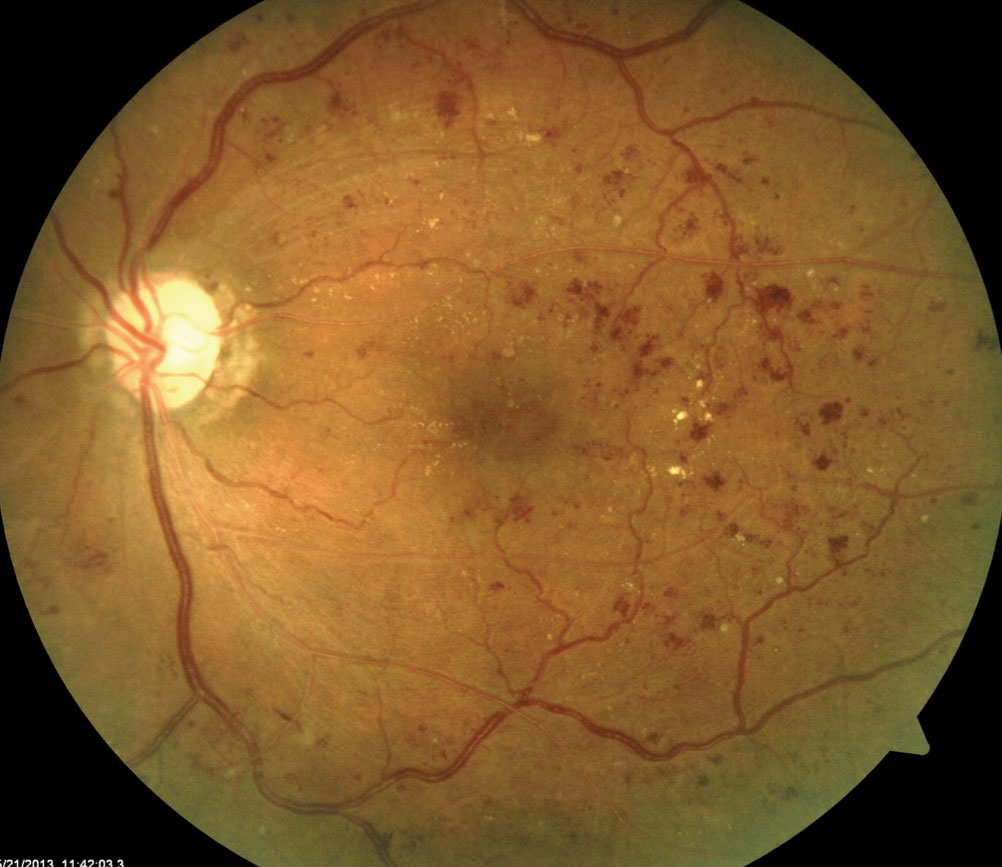
Vitreous hemorrhage: The new blood vessels may bleed into the vitreous humour, which causes dark spots (floaters). In more-severe cases, blood can fill the vitreous cavity and completely block your vision. In most cases, vitreous hemorrhage does not cause permanent vision loss, as the blood often clears from the eye within a few weeks or months. Unless your retina is damaged, your vision may return to its previous clarity.
Glaucoma: Pressure caused by this symptom can damage the optic nerve, as the new blood vessels growing in the front part of the patient’s eye may interfere with the normal flow of fluid out of the eye. This symptom develops into glaucoma.
Retinal detachment: This symptom may cause spots floating in your vision, flashes of light or severe vision loss, as the abnormal blood vessels associated with diabetic retinopathy stimulate the growth of scar tissue, which can pull the retina away from the back of the eye causing retinal detachment.
Blindness: Eventually, diabetic retinopathy, glaucoma or both can lead to complete vision loss.
What Are the Symptoms of Diabetic Retinopathy?
Diabetic retinopathy has no obvious symptoms and signs at its early stages, which means you will not be able to notice it at early stages. However, at advanced stages of diabetic retinopathy, patients might suffer from:
1- Gradually worsening vision.
2- Sudden vision loss.
3- Shapes floating in your field of vision (floaters).
4- Blurred or patchy vision.
5- Eye pain or redness.
6- Blurred vision.
7- Fluctuating vision.
8- Impaired color vision.
9- Dark or empty areas in your vision.
10- Vision loss.
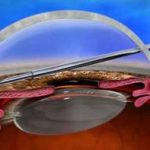
What are the recovery stages after the procedure?
Patients can return home on the same day or the day after surgical procedure. For the first couple of days after the surgery, the patient may be required to wear a patch over the treated eye, as activities such as watching television and reading can quickly tire their eyes. Blurred vision is expected after the procedure. However, the vision should improve gradually, and it may take several months to fully return to normal.
What are the risks and side effects of this procedure?
Risks and complications that might accompany vitreoretinal surgery may include:
Developing cataract, Eye Infection, Eye Bleeding, Retinal detachment, Fluid accumulation in the cornea.
In some cases, patients required further retinal surgery afterwards. However, the surgeon will explain the risks.
Why Iran for diabetic retinopathy?
Patients from all around the globe choose Iran over any other destination to go under the knife for the great reputation of Iran for performing the most delicate surgeries done by highly qualified surgeons at the most reasonable cost. Moreover, Iran is a great country for a vacation, as well as for taking a tour and getting to know all the great sites and adventures it offers, which makes your trip for pleasure too and not just for medical purposes.
How much does diabetic retinopathy treatment cost in Iran?
Treating diabetic retinopathy with eye injections costs between $150 to $400 per injection depending on the clinic and the condition. However, The cost of diabetic retinopathy surgical treatment is about $8,000 in the USA, $6,700 in Europe, $6,500 in Thailand and $4,000 in Turkey, while the cost of diabetic retinopathy treatment in Iran can be as low as $3,000.