ACL AND PCL SURGERY
What is the ACL?
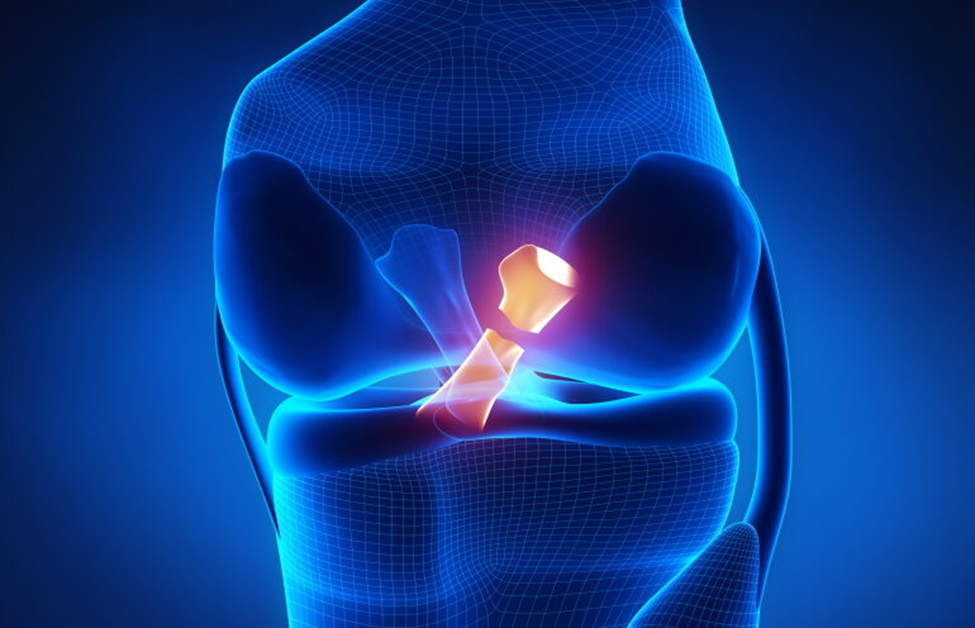
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) is one of the major stabilizing ligaments located centrally in the knee. It forms a central pivot along with the Posterior Cruciate Ligament surgery placed in a cruciate (cross) arrangement with each other.
Who are candidates for ACL surgery?
All people with a torn anterior cruciate ligament are candidates for surgery if non-surgical alternatives fail to provide the desired results. When you visit an orthopedist after a knee injury, he/she will evaluate your knee and the severity of the ligament tear and may ask that you undergo certain tests for this purpose. If the ligament is not completely torn, the specialist might prescribe medications and physiotherapy, or else he/she might recommend a surgical procedure.
The best candidates for a torn ACL surgery are:
1- Active adults
2- Children whose growth plates are closed
3- People who have symptoms of instability such as knee pain and knee buckling during physical activities
4- People who tried non-surgical ACL treatments such as physical therapy but didn’t get tangible results
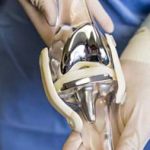
How Is Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Surgery Performed?
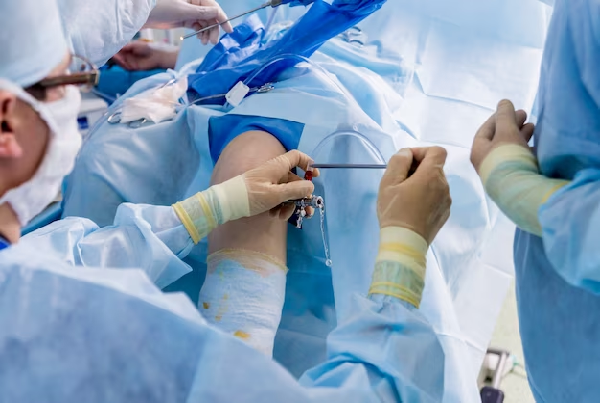
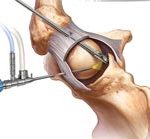
Depending on whether the ACL tear is partial or complete and other factors, orthopedic surgeons use different techniques in ACL surgery. While traditionally a knee surgery was performed through the open technique, with the advances in technology surgeons now often utilize arthroscopic surgery for an ACL tear repair, especially for partially torn ACLs.
An arthroscopic ACL surgery is a minimally-invasive procedure that involves creating small holes in the knee and repairing the torn ligament. Arthroscopic knee surgery can be done both under local and general anesthesia.
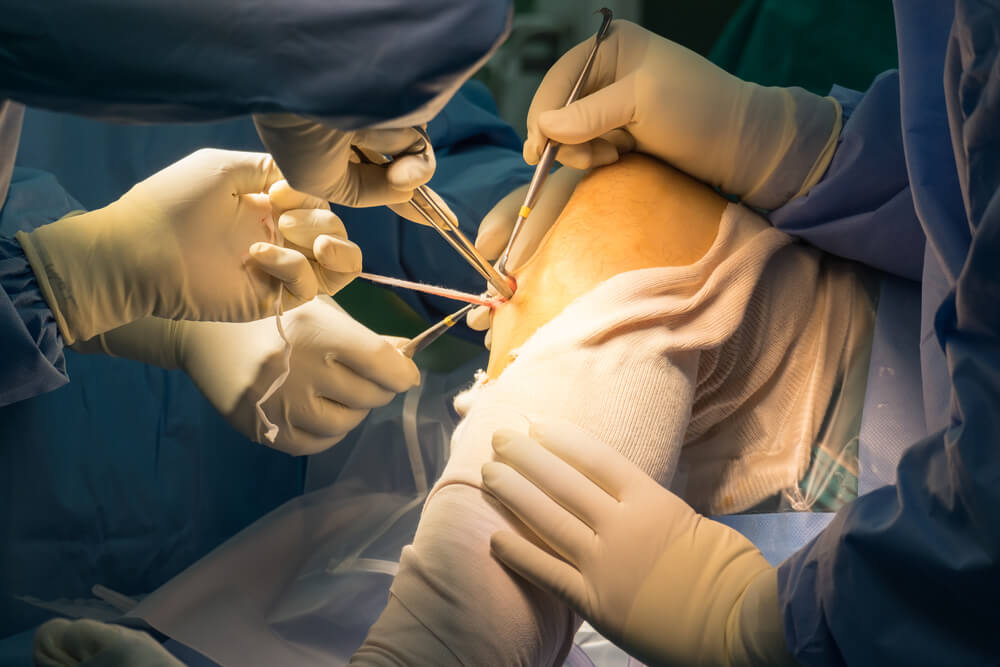
If the ligament is partially torn, the surgeon sutures the tissue back together and in cases that the ligament is completely torn, it should be replaced with a donor graft, which is usually taken from somewhere else in the patient’s body (called an autograft) or sometimes from another person (called an allograft).
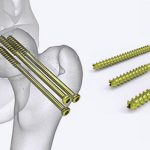
Grafts are usually extracted from patellar tendons (kneecap tendons), hamstring tendons, or quadriceps tendons. Autografts are typically used for adolescent or young patients and older patients usually need allografts. If the cruciate ligament is to be replaced with grafts, the surgeon drills two holes called ‘tunnels’ above and below the knee joint and places screws in them to anchor the grafts. This transplanted graft functions as a bridge on which the new ligament will gradually grow. After the completion of the surgery, the surgeon wraps a bandage around your knee and you will be sent to the recovery room to be under special care for 2-3 hours.
While the open ACL surgery might require staying in the hospital overnight, an arthroscopic surgery is usually done on an outpatient basis, meaning you won’t need to spend a night in the hospital.
Recovery and Aftercare
There might be some swelling, bruising, and numbness in your knee, shin, and ankle for a few days after surgery and you may feel tired for some time following an anterior cruciate ligament surgery. All these side effects will subside in a few days. You can apply ice on your lower leg to reduce swelling. It’s crucial to keep the incisions clean and dry to prevent infection. You will need to complete the physical therapy and rehabilitation courses prescribed by your surgeon in order to have a fast recovery. ACL surgery recovery takes a relatively long time and most patients will be able to return to normal activities in at least 6 months.
Risks and Complications
Although ACL reconstruction is a relatively safe procedure, there are potential risks and complications that might arise just as in any other surgery. Side effects and complications that might occur after anterior cruciate ligament surgery include:
– Infection
This rarely happens but if it does, it will be a serious problem. In cases that infection occurs inside the knee in the graft tendon, your body may not be able to effectively fight the infection and you may have to get the graft removed. You should let your doctor know if you notice any sign of infection including increasing pain and swelling, chills, and fever,
– Numbness
– Nerve or blood vessel injury
– Blood clots
– Loosening, stretching, scar tissue, or re-tear of the graft tendon, creating a need for a revision ACL surgery
Re-rupture of the cruciate ligament after surgery is uncommon, especially if an autograft is used as autografts are stronger than the original ACL. Possible causes of failure of ACL surgery are improper tension on the graft, suboptimal positioning of the graft, or improper fixation of the graft.
– Problems with the screws that hold the graft tendon
– Limited range of motion
– Stiffness (arthrofibrosis)
Stiffness after ACL repair is common but it can be easily addressed with rehabilitation. However, a type of stiffness called ‘cyclops lesion’ might not disappear with rehab and require arthroscopic surgery to be completely removed. This stiffness is a result of the formation of a ball of scar tissue in front of the knee, making you unable to fully straighten your knee after surgery.
– Crepitus (grating) of the kneecap when it moves against the lower end of the femur (thigh bone)
– Pain
– Anesthesia risks
It is very important to carefully follow the instructions of your surgeon to prevent post-op ACL surgery complications. Choosing a qualified and experienced orthopedic surgeon is also a major factor in reducing the chances of developing complications after ACL reconstruction surgery.
Why Iran?
There are great orthopedic surgeons and top-notch hospitals in Iran offering ACL repair surgery at decent prices. There is also Iran’s hospitable people, rich culture, tourist attractions, and high travel safety. Taken together, these are convincing reasons to choose Iran for an anterior cruciate ligament repair experience.
Cost in Iran
Prices for ACL surgery in Iran go from $1000 to $3000 depending on the severity of the knee sprain, the hospital, and the expertise of the surgeon. This is, of course, the cost of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in Iran for foreign patients without insurance and it includes all related expenses such as anesthesia, hospital fees, etc. The cost of surgery for other ligament and meniscus injuries including posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) in Iran is typically within the same range. If we compare the average cost of an ACL repair surgery in Iran with that in other countries, we see that Iran is an ideal option for patients who are looking for an affordable solution to their keen injury problem. For an ACL reconstruction surgery in the US, a patient who isn’t covered by insurance has to pay at least $13000, which even doesn’t include the cost of anesthesia and other hospital expenses. A torn cruciate ligament surgery in Turkey, Mexico, and Australia costs $5000, $6000, and $9000 on average.